E4SMA has developed a global, multi-regional energy systems model optimized for customization.
Also, we are expert users of the ETSAP-TIAM global model.
Our basic model fully relies on open-source data and has open access. We have also developed customized versions that use data from private sources and are accessible to clients only.
GEM (Global Energy Model)
Coverage: Global multiregional (23-31 regions) | Model type: TIMES | Horizon: 2019-2100
The global model is designed to enable comprehensive scenario analyses. It enables users to identify pathways to reach a 1.5-degree climate goal. The features of the model allow for identifying ways to achieve this target in a socially, economically, and technically feasible manner.
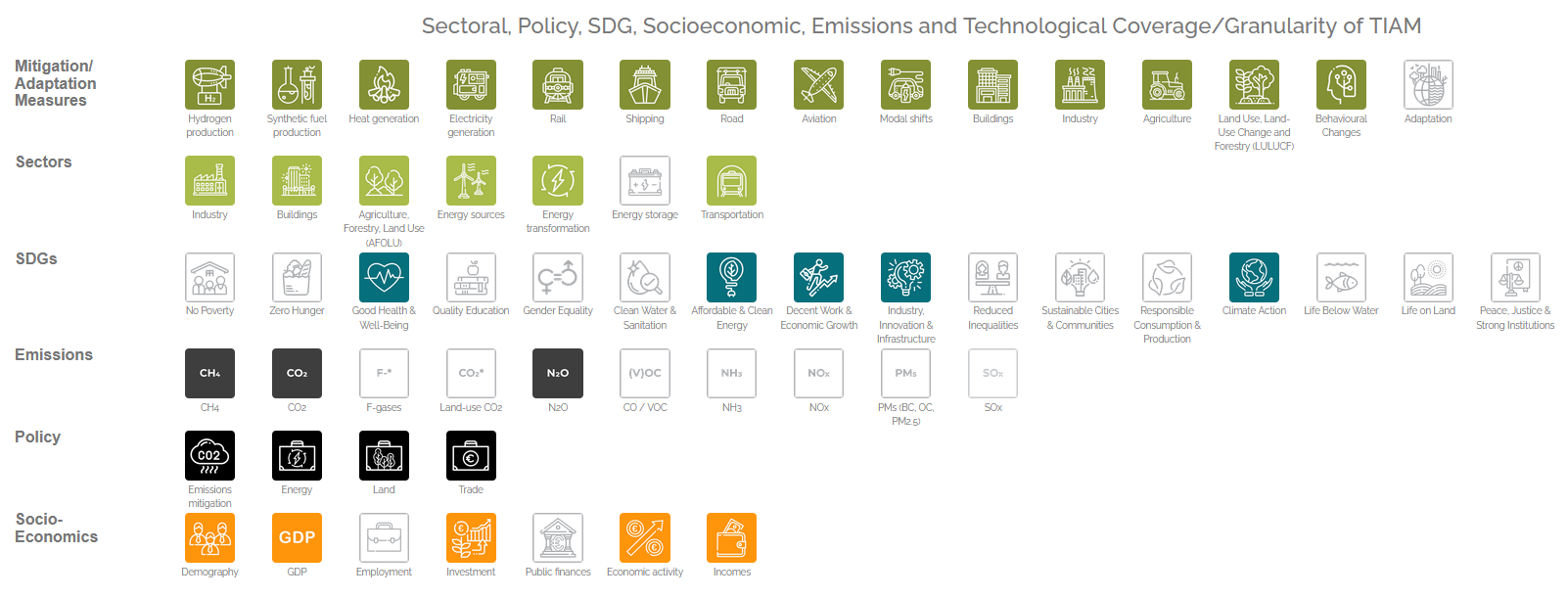
We have equipped the model with an explicit representation of 23-31 different regions (flexible) covering the entire globe with options to mitigate CO2 and non-CO2 greenhouse gases.
Also, the model covers the full energy system represented in seven energy sectors, divided into two supply side and five demand sectors.
The global model covers the economy, environment, and climate systems. Correspondingly, the model enables modellers to explore multiple climate mitigation pathways and assess the transition toward the United Nations’ sustainable development goals.
The structure of the global model is optimal for linking to economic models. This makes the model fit for global policy analysis and assessment of nationally determined contributions.
Likewise, the model can be used for contributions to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) assessment reports. The model can be made consistent with Shared Socioeconomic Pathways narratives (SSPs) and benchmarked against current data and the SSP marker models.
Correspondingly, users are able to determine the impacts that radical decarbonization of the energy system will have on the structure of the economic system, public health, and public and private investment decisions. Likewise, the trade-offs and co-benefits of the transition to an environmentally sustainable shared socio-economic pathway can be determined.
The global model is an integrated assessment model. We have developed it using the TIMES modelling framework, the user interface VEDA2.0 for data handling, and the GAMS/CPLEX modelling language and optimizer.
Main features of our global model:
- Extended geographical representation with flexible representation which spans from 23 to 31 regions
- The horizon spans from 2019-2100
- Flexibility of the power sector assessed through 20 time slices (four seasons and five intra-days slices)
- The base year templates parametrically link to internationally recognized energy balances and energy statistics where the base year and regional aggregation can relatively easily be changed.
- Power sector calibrated utilizing explicit power plant portfolios
- Upstream sector based on the latest IEA World Energy Outlook fuel prices
- Detailed representation of most innovative mitigation options and fuels, including hydrogen, bio-energies, and e-fuels
- New technology repository databases based on publicly available sources like the EU Reference scenario 2020 and the IEA ETSAP Technology briefs.
- Automated commodity and process naming convention dictionaries.
Features supporting customization:
- Built with a modular approach, which facilitates i) multiple scenario explorations, ii) input assumption maintenance, iii) review/improvement of some modelling components
- Model inputs designed to facilitate possible future recalibrations to most recent years.
- Regions defined by choosing the most relevant regional groupings and disaggregations. Furthermore, the model structure was designed to facilitate any possible future review of the regional disaggregation level.
- Time slices defined flexibly, allowing for easy revision.
- Designed to explicitly track stocks of most relevant technologies (e.g., power plant capacities, transport fleets, GW of installed boilers, etc.)
- Key data sources and assumptions clearly reported allowing for speeding up the learning curve and facilitating future usage and maintenance.
- Fully documented through a standard model manual that guides users through the high-level model design and serves as a basic operational manual for users.
The ETSAP-TIAM global model
Coverage: Global multiregional (15 regions) | Model type: TIMES | Horizon: 2005-2100
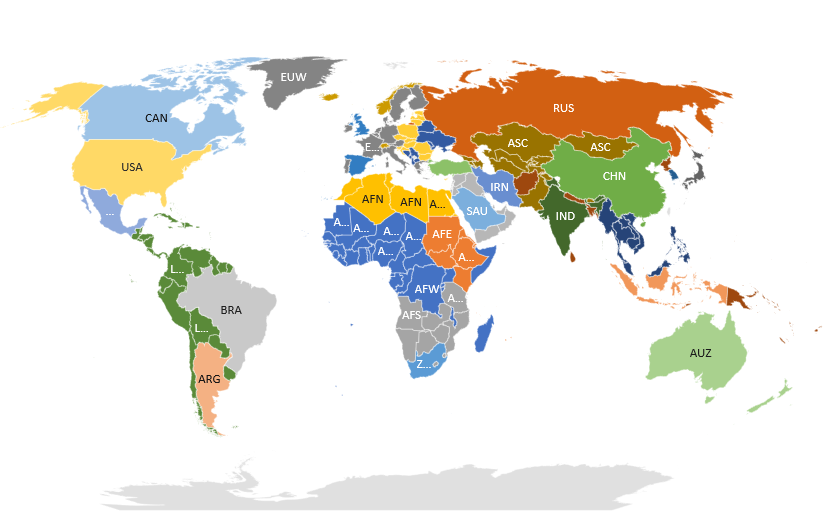
The ETSAP-TIAM (TIMES Integrated Assessment Model) is a well-established, multi-region, global version of the TIMES model, developed by the IEA-ETSAP Community.
The ETSAP-TIAM model combines an energy system representation of fifteen different regions with options to mitigate energy-related CO2, non-CO2 greenhouse gases, and non-energy CO2 mitigation options, such as afforestation.
Key features of the TIAM model
- Covers the entire globe, via fifteen regions.
- Features a detailed representation of services and technologies in the energy sector.
- The time horizon spans from 2005 to 2100 and is divided into a user-chosen number of time periods.
- Six time-slices, representing summer daytime, summer nighttime, winter daytime, winter nighttime, “transition season” daytime and nighttime.
- The climate module calculates changes in the atmospheric concentration of CO2, CH4 and N2O, and as a consequence the change in atmospheric radiative forcing compared to pre-industrial times, and finally the temperature change over pre-industrial times for the atmosphere and the deep ocean.
- The economic, population and sectoral growths are used to determine specific drivers for the growth in energy demands in a “reference” scenario where no climate change mitigation takes place.
- A technology-rich model that represents most major fossil fuel and low-carbon technologies that are envisaged to be available for at least the first half of the 21st century.
Detailed documentation on the model is available on the I2AMParis platform.